
Testifying or Consulting Experts
We review your data and, backed with research and experience, provide you with a verbal or written summary or report of our findings after discussing them verbally with you and obtaining your authorization. We either provide our own conclusions or confirm the conclusion(s) of your original expert and identify the strengths and weaknesses of the issues in dispute with supporting references either as consultants or testifying experts.
Obtain our Annotated Handbook of Advanced Fire & Explosion Investigation and Litigation free of charge by sending a request to [email protected] .
Fire Modeling
Fire modeling is a scientific approach that uses computational methods and mathematical equations to simulate and predict the behavior of fires. It involves analyzing various factors such as fuel types, weather conditions, topography, and fire spread patterns to understand how fires evolve and spread in a specific area. Fire modelling produces graphical representations that can effectively convey technical information to the layperson, assist in understanding how a fire may have evolved and assess the relationship between the heat release rate of the burning fuel and other variables (e.g. fire spread, tenability, etc.)
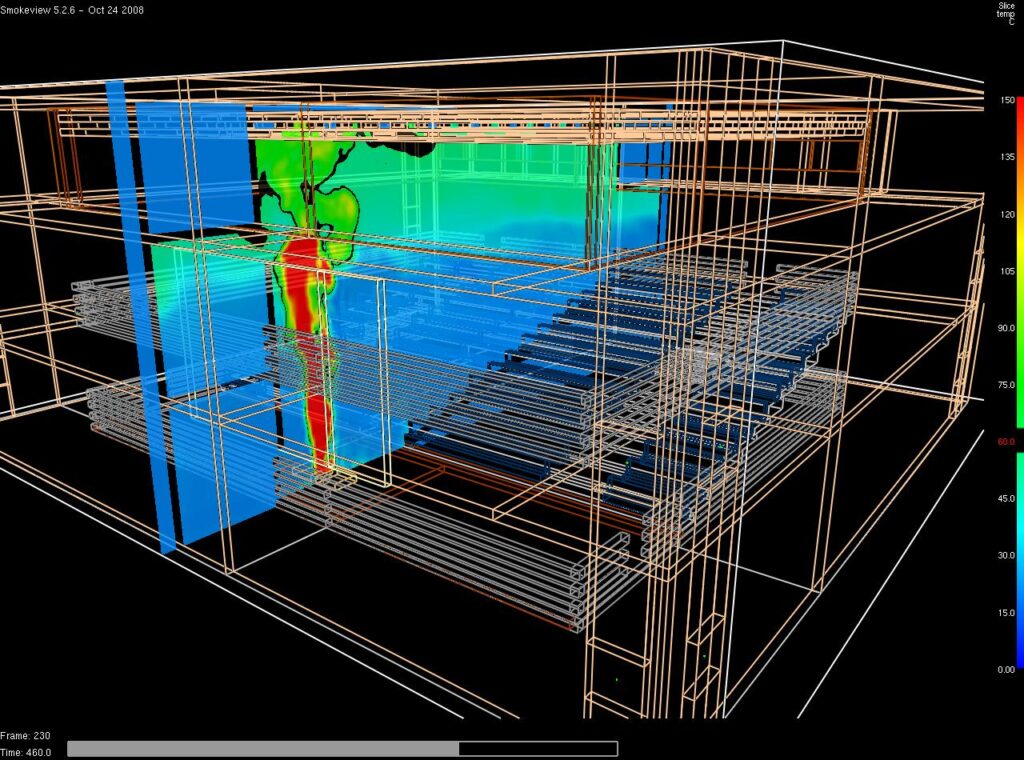

Tenability – Fire Death & Injuries
A fire becomes untenable when physical conditions in a room or building threaten the safety, health, or life of persons or impairs their ability to escape from a room, residence, or building. Incapacitation occurs when an occupant is no longer capable of self-preservation because of exposure to heat, smoke, or toxic gases in a fire. The threshold at which an environment becomes untenable varies with the individual, the building, and the fire. The answer to this and related questions requires knowledge of the building, the fire, the location, movement, and actions of the occupant during the fire, the tenability conditions that existed throughout the fire’s development, and the collective impact of those conditions on the occupant.
Artificial Intelligence in Fire and Explosion Investigation and Litigation
AI empowers investigators to analyze vast quantities of digital evidence rapidly and accurately, to research and gather data, generate hypotheses, make decisions, and develop strategies. AI’s ability to manage repetitive and mundane tasks, such as writing and reviewing reports, allows investigators to dedicate more time to critical thinking and problem-solving, resulting in faster and more accurate investigation outcomes.
